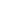Breast Cancer


Breast imaging
Breast cancer takes years to develop and very small lumps may not be felt on examination. The various breast imaging techniques available at NMC Royal Hospital include:
X-ray Mammography

A safe and effective x-ray technique that can spot a cancerous lesion long before a lump can be seen or felt. The test involves compressing the breast for a few seconds while pictures are taken. NMC Royal’s advanced Mammography Unit ensures high quality images with extremely low levels of radiation.
Sonomammography
Ultrasound examination of the breasts is often used as an adjunct to X-ray Mammography. It is particularly helpful in younger women who have dense breasts.
MR Mammography
Magnetic Resonance Imaging provides detailed, cross-sectional images. It can differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, and is especially useful in detecting implant failure.
Scintimammography
Scintimammography is an exciting new Nuclear Medicine scan that identifies cancer cells. These scans are very sensitive and beneficial in cases where x-ray mammography and other investigations prove unhelpful. They are of particular value in women with dense breasts and in those who have had previous surgery and/or implants.
NMC Royal Hospital and Breast Cancer
At NMC Royal Hospital, we know that early detection of breast cancer is one of the best ways to prevent its spread and ensure a successful treatment outcome. If detected early, patients can expect to live near normal lives with modern treatment methods.
NMC Royal Hospital offers the most comprehensive range of breast cancer services in UAE’s private health sector.
Our senior specialists have many years of experience in diagnosing and treating breast cancer.
The most advanced breast cancer screening and diagnostic techniques include:
- X-ray Mammography
- Sonomammography
- MR Mammography
- Scintimammography
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology(FNAC)
- Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
- Image-guided Breast Biopsy
- Cytology & Histopathology Service
- Appropriate, reliable and prompt treatment options
What is breast cancer?
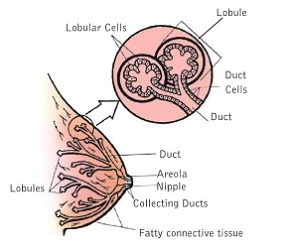
Breast cancer is a malignant tumour that develops from the cells of the breast. Nearly all breast cancers start in the lobules and ducts, which are the glands that produce milk and the tubes that connect them to the nipples.
How frequent is it?
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women. The incident is higher in western countries where it is estimated that one in nine women will get breast cancer.
It is also one of the leading causes of cancer deaths in women. Fortunately however, death rates are on the decline due to early detection and improved treatment.
What causes breast cancer?
The exact cause of breast cancer is not yet known. However, some of the important risk factors identified are as follows:
Family history. The risk increases when close blood relatives have this disease.
Genetic factors. Studies show that some breast cancer is linked to changes in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
Hormonal factors. Women who start periods early or haves a delayed menopause are at a higher risk. The same is true for women who have not had children or who had their first child after the age of 30.
Breast feeding. Some studies indicate that breast feeding reduces the risk.
Breast self-examination
 Stand in front of a mirror and look at each breast separately. Note the size, shape, colour, contour and direction of your breasts and nipples. Compare them and look for puckers, dimples or other changes.
Stand in front of a mirror and look at each breast separately. Note the size, shape, colour, contour and direction of your breasts and nipples. Compare them and look for puckers, dimples or other changes. Raise your arms over your head and look at your breasts, as you turn slowly from side to side.
Raise your arms over your head and look at your breasts, as you turn slowly from side to side.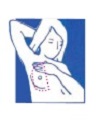 Stand in front of a mirror and start BSE just below the collar bone.
Stand in front of a mirror and start BSE just below the collar bone. Use the left hand for the right breast. Apply firm pressure and make small circles as you go back and forth (in an up or down, circular or spoke motion) in a pattern covering all the breast area including the nipple. Extend the examination to the breast tissue in the armpit. Change your hand and repeat BSE on the opposite breast.
Use the left hand for the right breast. Apply firm pressure and make small circles as you go back and forth (in an up or down, circular or spoke motion) in a pattern covering all the breast area including the nipple. Extend the examination to the breast tissue in the armpit. Change your hand and repeat BSE on the opposite breast. Lie down and raise one arm above your head. Examine your breast as before. Change the arm and repeat BSE on the opposite breast.
Lie down and raise one arm above your head. Examine your breast as before. Change the arm and repeat BSE on the opposite breast.
How is breast cancer detected?
The earlier breast cancer is detected, the better are the chances for successful treatment. The recommended guidelines for finding breast cancer early are:

- Women 40 and over should have a mammogram every year.
- Between the ages of 20 and 39, women should have their breasts examined by a doctor every 3 years. After age 40, this should be repeated every year.
- All women over 20 should do Breast Self-Examination (BSE) every month.
- The best time for BSE is about a week after the period ends, when the breasts are not tender or swollen. It should be repeated on the same day every month. BSE should be performed also during pregnancy and breast feeding, and by those who have breast implants.
Signs of breast cancer

By regularly examining your breasts, you are likely to notice any changes that may occur. The most common sign of breast cancer is a lump or mass. Other signs include a swelling of part of the breast, skin irritation or dimpling (the so-called orange skin), nipple pain or retraction, redness or scaling of the nipple or breast skin, and a discharge other than breast milk.
If a change is noticed, you should consult your doctor as soon a possible. Remember, however, that most of the time these changes are not cancer.